🔑 Key Learning
- Common soft tissue lumps of the wrist and hand, usually arising from herniation of the synovial lining.
- Typically asymptomatic, but can cause pain or joint restriction if large.
-
Transillumination helps differentiate them from solid masses.
- Most resolve without treatment, but options include aspiration or surgical excision if symptomatic.
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Ganglion cysts arise from outpouching of synovial fluid from a joint capsule or tendon sheath.
- The cyst contains gelatinous synovial fluid and is lined by flattened connective tissue rather than true epithelium.
-
Myxoid (mucous) cysts are a subtype typically found near the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints, associated with osteoarthritis.
👀 Clinical Features
- Common sites:
- Dorsum of the wrist (most common)
- Volar aspect of wrist (near the radial artery)
- Base of the fingers or over DIP joints (in the case of mucous cysts)
- Typically painless, but may cause:
- Cosmetic concern
- Local discomfort or aching
- Restricted joint movement if large or impinging on structures
- On examination:
- Smooth, round, mobile, cystic swelling
-
Transilluminates due to fluid content
- Tethered to underlying structures
- Myxoid cysts may express clear, jelly-like fluid if ruptured
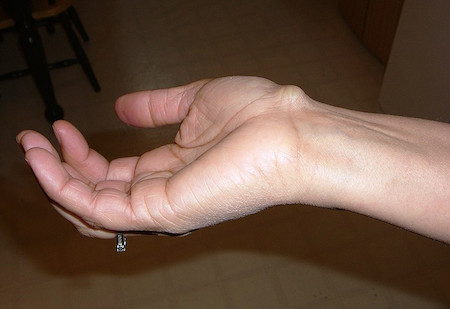 Figure 170: Ganglion cyst. User:GEMalone, Cyst Profile2, CC BY 3.0
Figure 170: Ganglion cyst. User:GEMalone, Cyst Profile2, CC BY 3.0
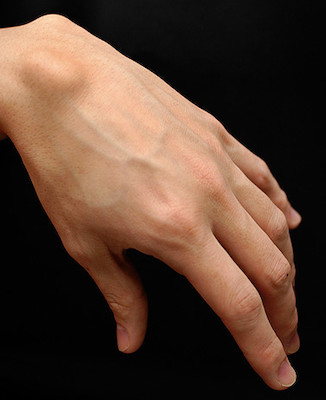 Figure 171: Ganglion-cyst, Esturcke at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0
Figure 171: Ganglion-cyst, Esturcke at English Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0
🧪 Investigations
- Diagnosis is clinical
- Ultrasound can confirm cystic nature and differentiate from solid masses
- Imaging may be considered if diagnosis is uncertain or deep cyst suspected (e.g. MRI)
💊 Management
- Reassurance: Most resolve spontaneously
- Conservative:
- Watch and wait if asymptomatic
- Aspiration:
- High recurrence rate (~50%)
- Surgical excision:
- Indicated for:
- Persistent pain
- Functional impairment
- Cosmetic concern with recurrence
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- Transilluminating soft swelling on wrist → Ganglion cyst
- Lump over DIP joint + clear fluid leakage → Myxoid cyst (associated with OA)


