🔑 Key Learning
-
Vasospastic disorder affecting the fingers and toes
-
Triggered by cold or emotional stress → white/pale, painful, numb
-
Can be primary or secondary (especially connective tissue diseases)
-
1st line treatment = nifedipine (CCB)
🧬 Pathophysiology
-
Cold or stress triggers excessive vasoconstriction of digital arteries
-
Results in transient ischaemia followed by reperfusion
👀 Clinical Features
-
Classic triphasic colour change of digits:
-
White (pallor) – due to ischaemia
-
Blue (cyanosis) – due to deoxygenated blood
-
Red (hyperaemia) – on rewarming
-
Associated symptoms: pain, tingling, numbness
-
Often symmetrical in primary, asymmetrical in secondary
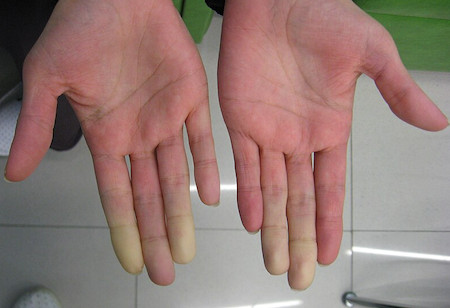 Figure 173: Secondary Raynaud's in Sjögren's syndrome, Intermedichbo, CC BY-SA 3.0
Figure 173: Secondary Raynaud's in Sjögren's syndrome, Intermedichbo, CC BY-SA 3.0
💡 Causes
Primary Raynaud’s (Raynaud’s Disease)
-
Idiopathic, more common in young women
-
Usually mild
Secondary Raynaud’s (Raynaud’s Phenomenon)
-
Associated with underlying disease. Long list of causes. Commonly:
-
Systemic sclerosis
-
SLE
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
💊 Management
-
1st line: Nifedipine (calcium channel blocker)
-
2nd line: IV prostacyclin (epoprostenol) infusion (for severe cases)
-
Advise on lifestyle: keeping hands warm, smoking cessation
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- Triphasic colour change, pain, numbness triggered by cold → think Raynaud’s
- 1st line treatment: nifedipine

