🔑 Key Learning
- Antepartum haemorrhage (APH) = bleeding after 24 weeks gestation and before delivery.
- Three key causes: placental abruption (painful, firm 'woody' uterus), placenta praevia (painless, visible bleeding), vasa praevia (rupture → fetal distress).
- Placental abruption = emergency; often concealed bleed and maternal compromise.
- Placenta praevia = painless bleeding; managed with serial TVUS and elective C-section.
- Vasa praevia = painless bleed + fetal bradycardia post-ROM; requires C-section at 34–36 weeks.
🧬 Placental Abruption
🧠 Pathophysiology
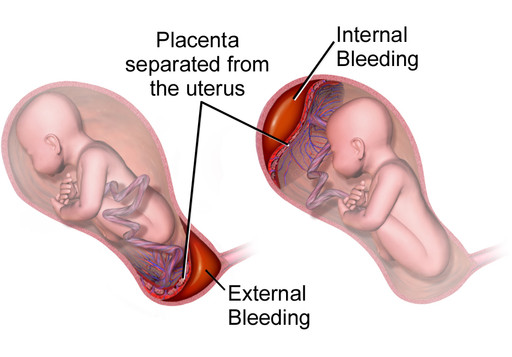
Separation of the placenta from the uterine wall, leading to haemorrhage:
- Revealed: PV bleeding is visible.
- Concealed: Cervical os closed → blood trapped in uterus → abdominal pain and shock.
⚠️ Risk Factors
- Previous abruption
- Pre-eclampsia
- Multiple pregnancy
- Maternal age
- Smoking
👀 Clinical Features
- Sudden, severe continuous abdominal pain
- PV bleeding (remember - bleeding may be absent if concealed)
- Tender, woody uterus
- Shock: hypotension, tachycardia
🧪 Investigations
- Diagnosis is clinical
- Ultrasound to rule out placenta praevia
- CTG: fetal monitoring
💊 Management
- Maternal resuscitation and transfusion
- Foetal distress → emergency C-section
-
No foetal distress:
- > 37 weeks → induce labour
- < 37 weeks → admit, give corticosteroids
📍 Placenta Praevia
🧠 Pathophysiology
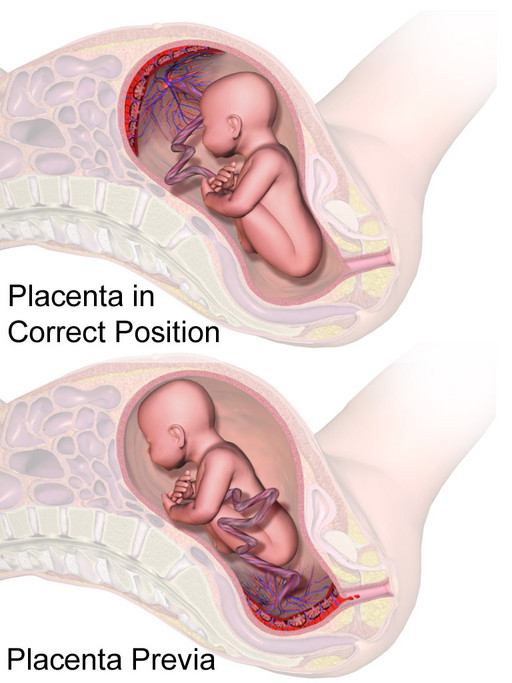
- Placenta praevia: placenta covers the cervical os
- Low lying placenta: placenta within 20mm of os but not covering
⚠️ Risk Factors
- Previous C-section
- Uterine abnormalities e.g. fibroids
👀 Clinical Features
- Painless, visible PV bleeding
- Usually presents after 35 weeks
🧪 Investigations
- Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) = diagnostic test of choice
💊 Management
- If identified during routine scanning, TVUS follow-up is recommended at 32 and 36 weeks
- Planned C-section at 36–37 weeks to reduce risk of severe bleeding
- Corticosteroids for fetal lung maturation
🩸 Vasa Praevia
🧠 Pathophysiology
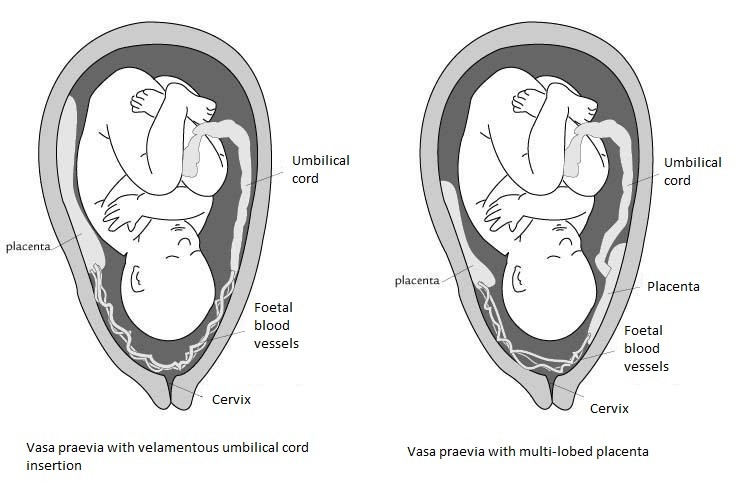
- Fetal vessels traverse membranes near cervical os → at risk of bleeding, particularly when there is rupture of membranes during labour.
👀 Clinical Features
-
Triad:
- Following rupture of membranes
- Painless vaginal bleeding
- Foetal bradycardia/distress
💊 Management
- Planned C-section at 34–36 weeks
- Corticosteroids for fetal lung development
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- Woody uterus, severe pain, concealed bleed → placental abruption
- Painless PV bleeding, 36 weeks → placenta praevia
- ROM + painless bleeding + fetal distress → vasa praevia
- Abruption + fetal distress → emergency C-section
-
Placenta praevia diagnosed at 20-week scan → repeat TVUS at 32 and 36 weeks
- Planned C-section at 36–37 weeks
- Planned C-section at 36–37 weeks
