🔑 Key Learning
-
Menopause is diagnosed after 12 months of amenorrhoea.
-
Premature menopause = under 40 years
- Early = 40–45 years.
-
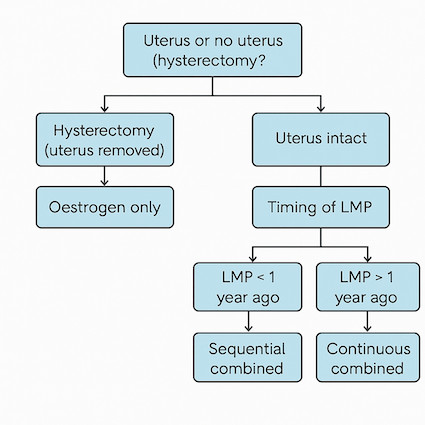
HRT is tailored based on uterus status and timing of last menstrual period. For the exam, the most important thing to remember is:
- No uterus? Oestrogen only
- Uterus intact. LMP < 1 year ago - Sequential combined HRT
- Uterus intact. LMP > 1 year ago - Continuous combined HRT
-
Transdermal oestrogen avoids increased VTE risk.
-
Vaginal oestrogen is 1st line for isolated genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM).
🧬 Pathophysiology
-
Permanent cessation of menstruation due to follicular depletion.
-
Perimenopause = time before menopause, with cycle changes and vasomotor symptoms.
👀 Clinical Features
-
Irregular or changing menstrual cycles (lengthening/shortening).
-
Vasomotor symptoms: hot flushes, night sweats.
-
Mood: low mood, irritability, anxiety, mood swings.
-
Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause:
-
Vaginal dryness, soreness, itching
-
Dyspareunia
-
Post-coital bleeding
-
On exam: pale, dry vaginal walls with contact bleeding
-
Reduced libido
🧪 Diagnosis
-
Clinical diagnosis if classic symptoms in a woman > 45
-
FSH measurement is not essential in typical cases, but can aid diagnosis in specific situations:
-
Age > 45 with atypical symptoms
-
Age 40–45 if early menopause suspected
-
Age < 40 with suspected premature ovarian insufficiency
-
FSH > 30 IU/L on 2 occasions, 6 weeks apart → ovarian insufficiency
🚫 Contraception
- Women may remain fertile up to 2 years following their LMP, so contraception counselling is essential:
- Women < 50: use contraception for 2 years after LMP
-
Women > 50: continue for 1 year after LMP
- Options:
- POP can be used alongside cyclical HRT
-
COCP can be used in < 50s as alternative to HRT, but switch to POP after 50
💊 Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Backgroud
- Oestrogen replacement treats menopausal symptoms
- Progesterone protects the uterus - unopposed oestrogen causes endometrial thickening, increasing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma.
- Hence, no uterus? No need for progesterone.
Decision Tree
-
Uterus removed (hysterectomy) → oestrogen only HRT
-
Uterus intact → combined oestrogen + progestogen HRT
Based on timing of menopause:
-
LMP < 1 year ago → sequential combined HRT
- Designed to mimic natural menstrual cycle - periods of oestrogen followed by progestogen.
- Daily oestrogen, cyclical progestogen
-
Results in monthly bleed
-
LMP > 1 year ago → continuous combined HRT
-
Daily oestrogen and progestogen
-
No withdrawal bleed
Duration
-
Continue as long as needed for symptom relief
- Most commonly it's taken for 2 to 5 years
-
Premature menopause: continue until at least age 51 (reduce risk of osteoporosis etc.)
Route
-
Oral or transdermal (gel, spray, patch)
-
Transdermal oestrogen is preferred - unlike oral, it is NOT associated with increased VTE risk
❌ Contraindications to HRT
-
History of breast
- History of endometrial cancer or untreated endometrial hyperplasia
-
Undiagnosed PV bleeding or breast lump
-
History of VTE or thrombophilia
- Arterial thromboemolic disease: Ischaemic heart disease, stroke, or angina
-
Active liver disease
-
Pregnancy
- Caution is recommended with: Porphyria cutanea tarda, diabetes (CVD risk), VTE risk factors, history endometrial hyperplasia, migraines, RFs for breast cancer.
⚠️ Side Effects
-
Oestrogen: breast tenderness, bloating, fluid retention
-
Progestogen: mood changes, acne, breast pain
-
Irregular bleeding, especially with continuous combined HRT in first 4–6 months
🩸 Unscheduled Bleeding
- VERY common - up to 40% of women have unscheduled bleeding in the first 6 months of starting HRT.
- However, prolonged, or heavy bleeding, or persistent (e.g. daily) is not normal and may suggest underlying endometrial carcinoma.
- Assessment of risk factors is essential and determines risk/ investigation / 2WW referral.
- The British Menopause Society have produced the following guidelines.
🌡️ Non-Hormonal Alternatives
Vasomotor symptoms
-
SSRI/SNRI: fluoxetine, paroxetine, venlafaxine
-
Clonidine
-
Gabapentin
-
CBT
Mood symptoms
-
Treat with antidepressants as required
💧 Management of Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause
-
1st Line: Low-dose vaginal oestrogen
-
2nd Line: Oral ospemifene (SERM)
-
Vaginal moisturisers and lubricants can be used alone or with vaginal oestrogen
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
-
LMP > 1 year ago + uterus intact → continuous combined HRT
-
LMP < 1 year ago → sequential HRT
-
Hysterectomy → oestrogen only HRT
-
Vaginal symptoms → vaginal oestrogen, safe even with systemic HRT
-
Transdermal oestrogen avoids VTE risk (unlike oral)
🔗 Useful Links and References

