🔑 Key Learning
- Common causes include rotator cuff disorders, adhesive capsulitis, osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint, and AC joint pathology.
- RC tendinopathy causes subacromial pain and painful arc.
- Adhesive capsulitis presents with progressive stiffness and loss of external rotation.
- OA of the GH joint causes global stiffness and joint space narrowing on XR.
- AC joint pain is worse on cross-body movements and localised to the ACJ.
🧬 Pathophysiology
Shoulder pain can arise from tendons, joints, bursa or referred pain. Common pathologies affect the rotator cuff (RC), glenohumeral joint (GHJ), or acromioclavicular joint (ACJ).
🦴 Rotator Cuff Disorders
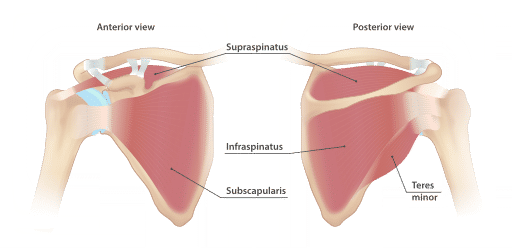
Anatomy
SITS muscles:
- Supraspinatus – ABduction (first 15°)
- Infraspinatus – External rotation
- Teres minor – ADduction and external rotation
- Subscapularis – Internal rotation and ADduction
.
🔥 Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy / Impingement
- Inflammation/tendinopathy of the RC tendons beneath the acromion.
- RFs: Age 35–80, repetitive overhead use, athletes.
👀 Clinical Features
- Lateral shoulder pain (esp. subacromial)
- Worse with overhead movement
- Night pain common
🧪 Examination
- Painful arc (70–120°)
- Pain on resisted abduction
- Painful active and passive ROM
💊 Management
- Analgesia:
- 1st line: Paracetamol
- 2nd line: Oral NSAID or codeine
- Physiotherapy
- Subacromial corticosteroid injection if persistent
❌ Rotator Cuff Tear
- Often post-traumatic (e.g. fall/dislocation)
👀 Features
- Severe shoulder pain and marked weakness
- Inability to abduct above 90°
- Positive drop arm test
💊 Management
- Urgent ortho referral
🧊 Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
- Fibrosis of the GHJ capsule → pain + progressive stiffness
- Strongly associated with diabetes and thyroid disease
👀 Clinical Features
- Painful shoulder → becomes progressively stiff → limits daily activities
- External rotation particularly limited
📈 Course
- Painful phase (3–9 months) - Progressive shoulder pain, especially on movement
- Stiff phase (6–12 months) - Progressive stiffness and deteriorating range of movement which limits function
- Resolution phase (1–4 years) - Gradual improvement in stiffness and restoration of function
💊 Management
- Analgesia:
- 1st line Paracetamol
- 2nd line: oral NSAID/codeine
- Early physiotherapy
- Consider intra-articular corticosteroid
🦴 Glenohumeral Joint Osteoarthritis
- Often secondary to trauma or RC tear
- Primary GHJ OA is rare
👀 Features
- Age > 60
- Deep joint pain
- Markedly reduced ROM, esp. external rotation
- XR: LOSS (Loss of space, Osteophytes, Sclerosis, Subchondral cysts)
💊 Management
- 1st line: Paracetamol
- 2nd line: Topical NSAID
- 3rd line: Oral NSAID/codeine
- Intra-articular corticosteroid if inadequate relief
🧱 Acromioclavicular Joint Disorders
💢 ACJ Osteoarthritis
- RF: Age > 60, weightlifting
- Pain over ACJ, worse with overhead movement or cross-body adduction
💥 ACJ Injury
- Ligament/tendon injury after trauma or fall
- Tender ACJ, painful elevation
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- Lateral deltoid pain + painful arc + night pain → Rotator cuff tendinopathy
- Sudden shoulder pain following trauma + weakness/drop arm → Rotator cuff tear
- Gradual stiff shoulder + limited external rotation + diabetes → Adhesive capsulitis
- Deep joint pain + reduced global ROM + XR changes (LOSS) → Glenohumeral OA
- Pain localised to AC joint + worse on cross-body movement → ACJ pathology
