🔑 Key Learning
- Common causes include overuse injuries, inflammation, or biomechanical issues
🦵 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) 'Runners knee'
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Overuse injury due to inflammation of the patellofemoral joint
- Triggered by sudden increase in activity, muscle imbalance, prolonged kneeling
👀 Clinical Features
- Achy knee pain, felt behind the patella
- Worse with activity: walking, running, stairs, kneeling
🧪 Examination
- Pain on patellar edge palpation
- Anterior knee pain reproduced by squatting
💊 Management
- Conservative: activity modification, physiotherapy, NSAIDs
🦴 Osgood-Schlatter’s Disease
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Apophysitis at tibial tuberosity from traction stress during adolescence
👀 Clinical Features
- Affects children aged 10–16, more common in boys
- Pain over tibial tuberosity, worse after exercise/kneeling
🧪 Examination
- Tender, possibly swollen tibial tuberosity
- Pain with resisted knee extension

💊 Management
- Rest, physiotherapy, NSAIDs
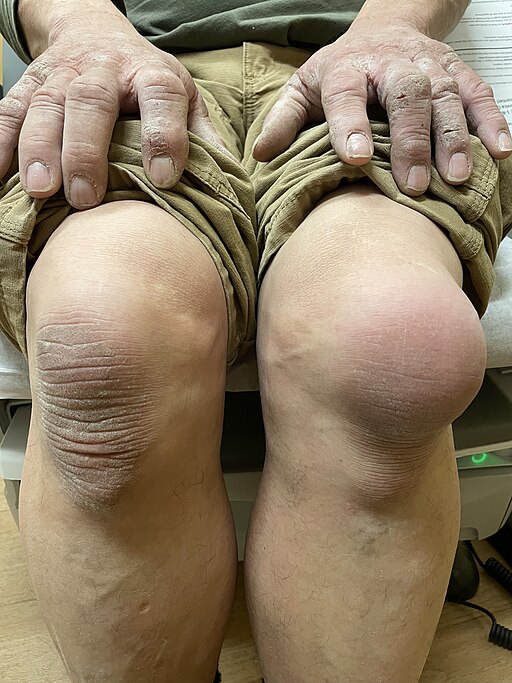
🧴 Prepatellar & Infrapatellar Bursitis
👀 Clinical Features
- Swelling and pain over anterior knee
- Prepatellar often post-trauma ('housemaid’s knee')
- Infrapatellar linked to kneeling at work (e.g. tilers, plumbers)
🧪 Examination
- Fluctuant anterior swelling
- May have signs of infection (fever, erythema)
💊 Management
- Aspiration if painful or ?infective
- Consider flucloxacillin if signs of infection
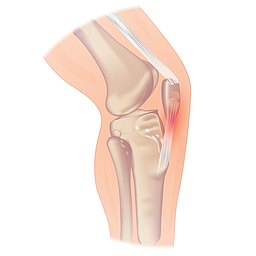
🦵 Patellar Tendonitis 'Jumpers knee'
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Overuse tendinopathy from jumping activities - MCQs may reference basketball etc.
👀 Clinical Features
- Anterior knee pain, worse with running/jumping, especially downhill
🧪 Examination
- Tenderness along patellar tendon
- Pain with resisted knee extension
💊 Management
- Relative rest, NSAIDs, physiotherapy
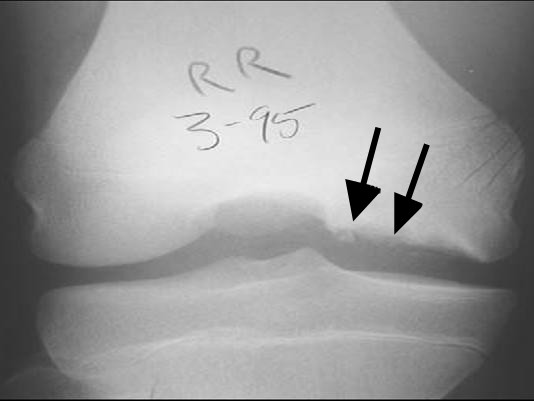
🦴 Osteochondritis Dissecans
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Subchondral bone necrosis due to impaired blood supply
- Dead fragments can detach into joint
👀 Clinical Features
- Joint pain, locking or catching sensations
🧪 Investigations
- X-ray: subchondral defects or loose bodies
🦵 Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS)
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Overuse friction injury between IT band and lateral femoral condyle
- History of increased activity - e,g, running

👀 Clinical Features
- Lateral knee pain, worsens with running or cycling
- Pain just proximal to the joint line
💊 Management
- Activity modification, ITB stretching, physiotherapy
💧 Baker’s Cyst
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Popliteal bursa swelling, often secondary to OA or meniscal injury
👀 Clinical Features
- Posterior knee swelling, can cause vague discomfort
- Sudden rupture can mimic DVT: calf swelling, erythema, pain
🧪 Investigations
- 1st line: Ultrasound to differentiate from DVT
💊 Management
- Reassurance if asymptomatic
- Treat underlying joint pathology
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- PFPS → anterior knee pain, behind patella, in runners, worse on stairs/kneeling
- Osgood-Schlatter’s → adolescent with tibial tuberosity pain post-sport
- Prepatellar bursitis → fluctuant anterior swelling, housemaid’s knee
- Patellar tendonitis → jumper’s knee, pain worse with resisted extension
- Osteochondritis dissecans → adolescent with knee locking/catching
- ITBS → lateral knee pain in runner, worse with flexion/extension
- Baker’s cyst → bulge in popliteal fossa
🔗 Useful Links and References
- NICE CKS. Knee pain - assessment
