🔑 Key Learning
- Developmental dysplasia of the hip
- 0-3 years
- Clinical features: Barlow, Ortolani positive.
- Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
- 4-8 years
- Clinical features: pain, stiffness, reduced ROM (esp. aBduction and internal rotation)
- X-ray: widened joint space, flattening of the femoral head
- Slipped upper femoral epiphysis (SUFE)
- 10-15 years
- RFs: Overweight
- Transient synovitis
- 2-10 years
- HPc: recent viral illness
- Septic arthritis - Always rule out septic arthritis in any child with fever and hip pain.
👶 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
Age range: 0–3 years
👀 Clinical Features
- Leg length discrepancy
- Restricted hip abduction
-
Positive Barlow's and Ortolani’s signs:
- Barlow’s sign positive - aDduct the hip with posterior pressure on the knee - a palpable sensation of subluxation/dislocation
- Ortolani’s sign positive - flex the hips and knees and apply anterior pressure on the greater trochanters - a clunk is felt when the femoral head is relocated into the acetabulum
🧪 Investigations
- <6 months: Hip ultrasound
- >6 months: AP pelvic X-ray
💊 Management
- <6 months: Pavlik harness
- 6–18 months: Closed reduction and hip spica
- >18 months or failed treatment: Open reduction ± reconstruction
🦵 Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Idiopathic avascular necrosis of the femoral head
Age range: 4–8 years
👀 Clinical Features
- Limp (often painless)
- Hip stiffness
- ↓ ROM – especially abduction and internal rotation
- Antalgic gait
🧪 Investigations
-
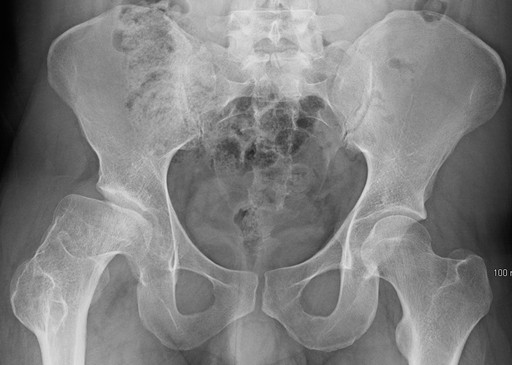
AP pelvis X-ray:
- Early: widened joint space
- Later: flattened femoral head
💊 Management
- Analgesia, physiotherapy, orthopaedic follow-up
- Surgery if severe deformity or older child
🦠 Transient Synovitis
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Benign inflammation of synovium, often post-viral
Age range: 2–10 years
👀 Clinical Features
- Sudden onset hip pain or limp
- May follow recent URTI
- ↓ ROM – esp. abduction
- Child appears well, afebrile or low-grade fever
🧪 Investigations
- Rule out septic arthritis: FBC/CRP, blood culture
- Hip US: may show effusion
💊 Management
- Rest and analgesia
- Self-resolving in 1–2 weeks
🍩 Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
🧬 Pathophysiology
- Posteroinferior slippage of femoral epiphysis on metaphysis
Age range: 10–15 years
⚠️ Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Male sex
- 20% bilateral
👀 Clinical Features
- Hip/knee pain
- Limp
- ↓ ROM – especially internal rotation and flexion
🧪 Investigations
- AP and frog-leg lateral pelvis X-rays
- Look for displacement and physeal widening
💊 Management
- Urgent surgical fixation (e.g. in-situ pinning) to prevent avascular necrosis
- Non-weight-bearing pre-op
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- Barlow + Ortolani positive in newborn → DDH
- 4–8 yr old, painless limp + restricted abduction/internal rotation → Perthes
- Post-viral limp in 6 yr old, afebrile → Transient synovitis
- Obese 12 yr old with knee pain and reduced hip IR → SUFE
- Febrile child with acutely irritable hip, ↑CRP/WCC → always rule out septic arthritis
