🔑 Key Learning
-
Breech = foetus positioned buttocks/feet-first; occurs in 3–4% of term pregnancies
- Types: Frank, Complete, Footling
- Diagnosis made via abdominal palpation, confirmed by ultrasound
- Management:
- <36 weeks: often resolves spontaneously
-
≥36 weeks: offer External Cephalic Version (ECV)
- If Rhesus-negative, ECV = indication for anti-D prophylaxis
- If ECV fails: consider C-section vs vaginal delivery (risk-balanced)
- Complications of breech delivery: head entrapment, cord prolapse, birth trauma, asphyxia
🧬 Definition and Types
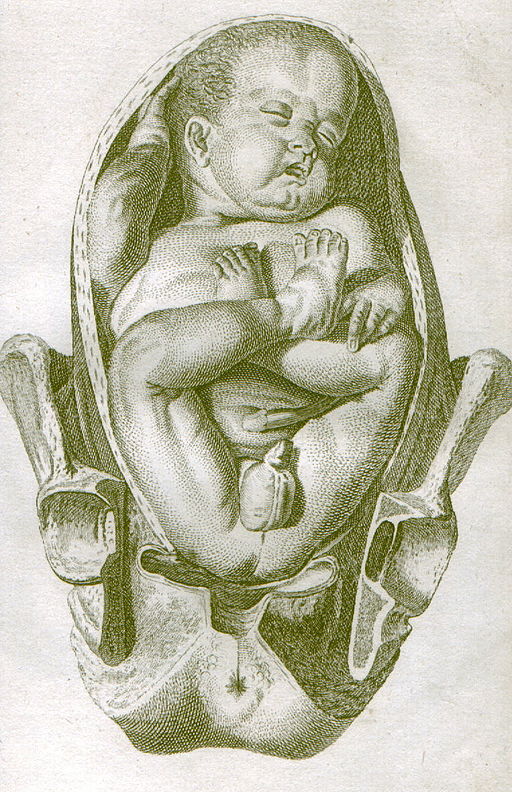
Breech = foetal buttocks or feet nearest the cervix
Types of Breech:
- Frank breech – hips flexed, knees extended (most common)
- Complete breech – hips and knees both flexed
- Footling breech – one or both feet presenting first
👀 Clinical Presentation
- Often asymptomatic, detected on routine antenatal palpation
- Suspected breech confirmed via ultrasound
- Foetal buttocks or feet palpable in maternal pelvis
💊 Management
<36 weeks gestation
- No intervention needed – likely to spontaneously rotate to cephalic
≥36 weeks (nulliparous) or ≥37 weeks (multiparous)
-
Offer ECV to turn foetus manually
- External cephalic version (ECV) attempts to turn the foetus to a cephalic (head-first) position by applying gentle pressure on the pregnant abdomen to manually rotate the foetus.
- The success rate is approximately 60%.
- Safer vaginal birth if successful
Failed ECV
-
Decision between:
- Planned C-section (safer for baby)
- Vaginal breech delivery (may be safer for mother)
🔴 Rhesus-negative mothers
- ECV is an indication for anti-D prophylaxis
- Prevents rhesus sensitisation (maternal antibodies against foetal RBCs)
⚠️ Complications
- Foetal head entrapment
- Umbilical cord prolapse
- Birth trauma (e.g. brachial plexus injury)
- Perinatal asphyxia
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
- Frank breech, hips flexed, knees extended → most common subtype
- ≥36 weeks, breech → offer ECV
- Rhesus-negative + ECV → give anti-D
- Failed ECV + breech + primiparous → likely C-section
