🔑 Key Learning
-
Common in the second trimester, especially between 12–22 weeks.
-
Caused by stretching of the round ligaments as the uterus grows.
-
Presents as sharp, stabbing groin pain triggered by movement.
-
Diagnosis is clinical; management is conservative with reassurance and analgesia.
🧬 Pathophysiology
-
The round ligaments connect the uterine horns to the labia majora via the inguinal canal.
-
As the uterus enlarges during pregnancy, these ligaments stretch and thicken.
-
Sudden movement (e.g. coughing, getting out of bed) can cause a brief spasm → sharp pain.
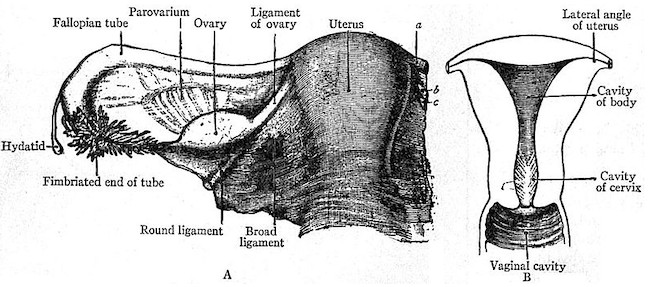 Figure 206: Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System, demonstrating the position of the round ligament.
Figure 206: Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System, demonstrating the position of the round ligament.
👀 Clinical Features
-
Onset typically in the second trimester (weeks 12–22)
-
Sharp or stabbing pain, often in the groin or lower abdomen (right side more common)
-
Pain is worsened by:
-
Standing up quickly
-
Coughing
-
Rolling in bed
-
May occur unilaterally or bilaterally
💊 Management
-
Conservative measures:
-
Reassurance
-
Rest and postural adjustments
-
Avoid sudden movements
-
Maternity support belts
-
Simple analgesia (e.g. paracetamol)
🔄 Differential Diagnosis: Pubic Symphysis Dysfunction
-
Caused by pregnancy-related ligamentous laxity
- Pain localised to pubic symphysis, may radiate to groin or thighs
- Clinical features:
- Waddling gait
-
Aggravated by walking or hip abduction
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
-
Pregnant woman, 2nd trimester, sudden groin pain triggered by movement → round ligament pain
-
Waddling gait + pubic tenderness → consider pubic symphysis dysfunction

