🔑 Key Learning
-
Caused by obstruction of the Bartholin's gland duct → mucus accumulation
-
Typically presents as a unilateral, medially protruding swelling at 4 or 8 o’clock position
-
May be asymptomatic, painful, or form an abscess
-
Management depends on symptoms: conservative, antibiotics, drainage, or marsupialisation
🧬 Pathophysiology
-
Bartholin's glands are located at the 4 and 8 o'clock positions of the vaginal introitus
-
They secrete mucus to lubricate the vulva and vaginal opening
-
Duct obstruction causes mucus buildup → cyst formation
-
If the cyst becomes infected → abscess develops, often painful and inflamed
👀 Clinical Features
-
Asymptomatic swelling: often incidental finding
-
Typical location: unilateral swelling at 4 or 8 o’clock on the inferior labia majora
-
Pain or tenderness: worsens with walking, sitting, or intercourse
-
Dyspareunia due to cyst proximity to vaginal opening
-
Bartholin's abscess: erythema, marked tenderness, possible fever
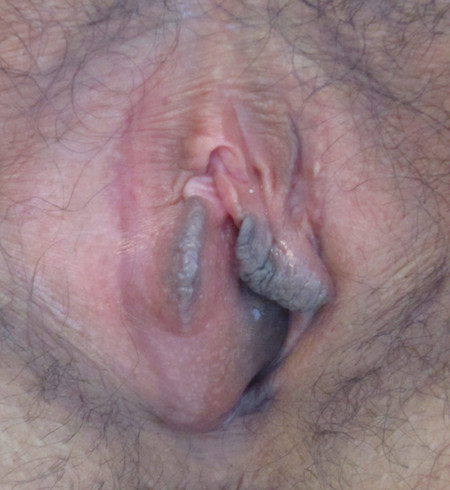 Figure 205: Right sided Bartholin cyst. Note the right sided bulge at "8 o'clock", protruding medially. Medimage, Barthonlincyst2011, CC BY-SA 3.0
Figure 205: Right sided Bartholin cyst. Note the right sided bulge at "8 o'clock", protruding medially. Medimage, Barthonlincyst2011, CC BY-SA 3.0
💊 Management
Conservative
-
Observation if small and asymptomatic
Medical
-
Oral antibiotics: if evidence of infection or abscess formation
Surgical
-
Incision and drainage: for painful or infected cysts
-
Word catheter: placed after drainage to allow continuous drainage and reduce recurrence risk
-
Marsupialisation: surgical creation of a new ductal opening, typically for recurrent cysts
📝 Exam Clues & Clinchers
-
Unilateral labial swelling at 4 or 8 o'clock position
-
Painful lump + fever = likely abscess → incision and drainage + Word catheter
-
Recurrent cysts → marsupialisation is definitive

